Due to continuous heavy rainfall in hilly regions, the water level of the Ravi River has risen significantly, raising concerns of floods in adjoining areas.
About Ravi River
- A transboundary river flowing through northwestern India and northeastern Pakistan.
- One of the five rivers of Punjab (Punjab = “Land of Five Rivers”).
Origin & Course
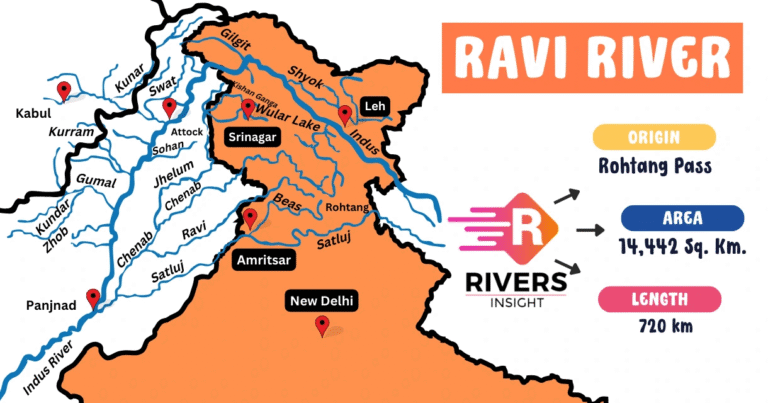
- Origin: Northern slopes of Rohtang Pass, Himachal Pradesh.
- Initially flows as two streams – Budhil and Tantgari – which later join.
- Passes through Chamba district (Himachal Pradesh) and receives many tributaries.
- Flows southward into Punjab, then enters Pakistan, where it merges with the Chenab River (a major Indus tributary).
Key Features
- Total Length: 720 km (India: 320 km).
- Catchment Area in India: 14,442 sq. km.
- Flow Pattern: Governed by snowmelt in spring and Southwest Monsoon rains (June–Sept.).
- Major Tributaries: Siul, Baira, and Ujh.
Dams & Projects
- Ranjit Sagar Dam (Thein Dam) – multipurpose (hydropower + irrigation).
- Chamera Dam Complex – Chamera I, II & III (hydropower projects).
Strategic Importance
- Under the Indus Water Treaty (1960), waters of Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej were allocated to India.
- Provides irrigation, hydropower, and drinking water to northwestern India.