The Union Minister of Coal and Mines highlighted that although coal is still crucial for India’s energy security, the government is promoting coal gasification as a cleaner alternative to reduce environmental challenges from conventional burning.
What is Coal Gasification?
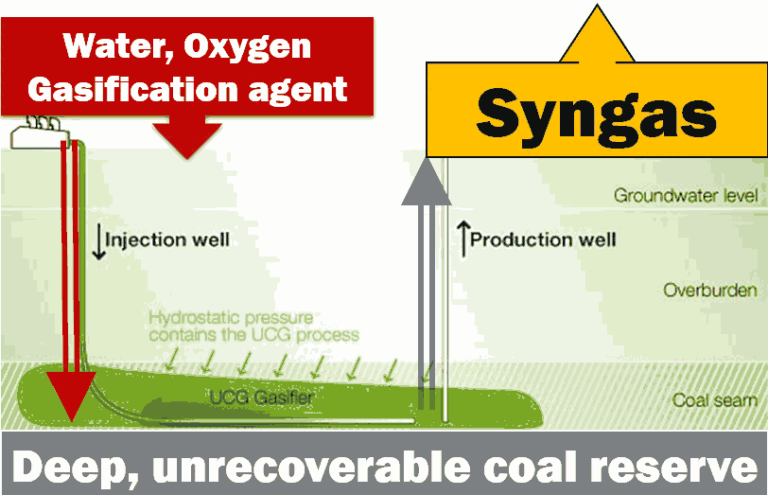
- Coal gasification is a technology that changes coal into synthesis gas (syngas), made up of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and hydrocarbons.
- Syngas can be used to:
- Generate electricity
- Produce liquid fuels
- Manufacture chemicals and fertilizers
- Unlike direct coal burning, this method leads to lower emissions of particulate matter and pollutants, making it comparatively eco-friendlier.
Government Measures to Boost Coal Gasification
- Auction Reforms: In commercial coal block auctions, firms committing to a set level of gasification receive a 50% rebate in revenue share.
- Target for 2030: India plans to achieve 100 million tonnes (MT) coal gasification by 2030, aiming to diversify coal use and reduce pollution.
- Financial Incentive Scheme (2024): Announced with a budget of ₹8,500 crore. Seeks participation of both public and private players to set up gasification plants across India.
Significance
- Reduces dependence on imported natural gas and crude oil.
- Provides cleaner fuel options while ensuring energy security.
- Encourages industrial growth through fertilizers, methanol, and chemical production.
Conclusion:
Coal gasification is being positioned as a bridge between India’s dependence on coal and its commitment to cleaner energy, supporting both environmental sustainability and economic growth.





