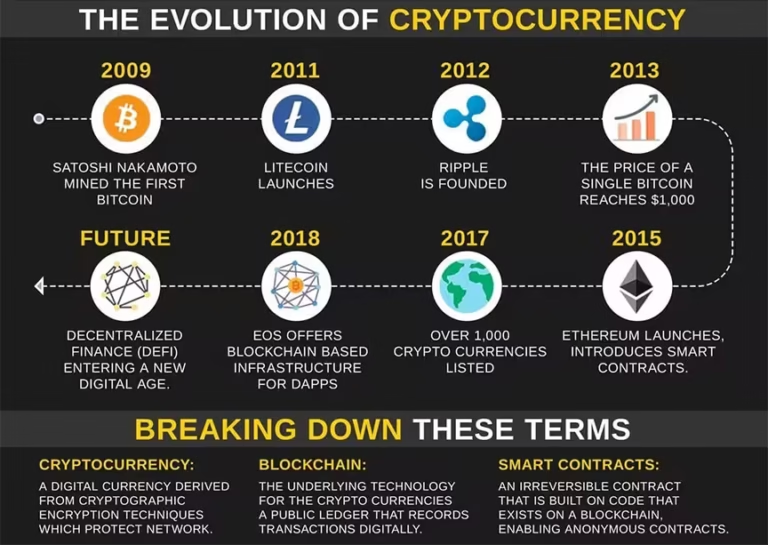
Cryptocurrency in India is expanding rapidly but the absence of clear legal provisions, concerns about financial stability, and rising cyber frauds have made it an important governance and economic policy issue.
What are Cryptocurrencies?
- Blockchain-based digital assets enabling decentralized, encrypted transactions.
- No legal tender status in India and not backed by any government or central authority.
- Value dependent on market demand, speculation, and global investor sentiment.
- Popular examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, largely traded on offshore platforms.
Crypto Exchanges
- Digital platforms enabling buying, selling, and storing of crypto assets.
- Operate without formal regulatory status in India.
- Wide accessibility via mobile apps attracts young investors, especially aged 18–35 years.
Reasons for Rising Crypto Scams in India
- Pump-and-dump schemes promoted by influencers.
- Social media traps through WhatsApp/Telegram promising high returns.
- Unregistered exchanges shutting down, leaving users with no legal remedy.
- Limited investor awareness and lack of financial literacy.
RBI's Major Concerns
- Threat to monetary sovereignty, as crypto bypasses official currency channels.
- Capital flight risk, enabling unrecorded cross-border money transfers.
- Extreme volatility, endangering financial stability and investor security.
- IMF also warns that digital currency growth may weaken monetary control and policy transmission.
Challenges in Crypto Regulation and Enforcement
- Data Issues: No mandatory disclosures or registration for crypto platforms. Jurisdictional issues with global exchanges.
- Digital Wallet Complexities: Self-custody wallets cannot be easily frozen or traced. Anonymous transactions and privacy coins hide user identity.
- Legal Limitations: India lacks a comprehensive cryptocurrency law. Current laws like PMLA and IT Act are insufficient for decentralized digital assets.
- Technical Barriers: Blockchain mixers, private coins, and encrypted wallets complicate investigations. Law agencies lack skilled manpower and adequate technical tools.
- Investor Risks: Highly volatile markets, no intrinsic value backing. Cyber hacks, phishing attacks, and permanent loss of private keys.
Way Forward
- Establish a dedicated cryptocurrency law and clear regulatory framework.
- Mandate registration and KYC compliance for all exchanges.
- Build cyber forensic capabilities and promote international cooperation.
- Encourage public awareness and financial literacy.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency represents innovation but also poses serious risks without proper safeguards. India must strike a fine balance between promoting digital progress and ensuring financial security and legal accountability.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.