A total lunar eclipse is expected in September 2025, during which the Moon will appear blood red. Millions across Asia and Europe will witness this rare astronomical event.
What is a Blood Moon?
- A Blood Moon refers to the reddish glow of the Moon seen during a total lunar eclipse.
- It occurs when Earth aligns between the Sun and the Moon, completely blocking direct sunlight.
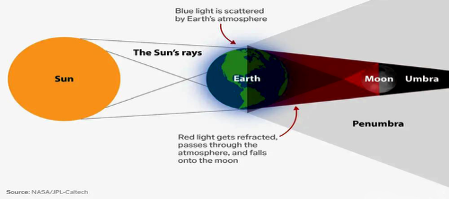
How Does it Occur?
- During the eclipse, sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere before reaching the Moon.
- Rayleigh scattering removes shorter blue wavelengths, while longer red wavelengths bend toward the Moon.
- As a result, the Moon appears red, orange, or copper in colour.
- The effect is strongest when the Moon is in Earth’s umbra (the darkest part of its shadow).
Factors Affecting Appearance
- Atmospheric conditions, dust, and pollution levels can alter the Moon’s shade.
- It may look deep red, bright orange, or dull copper, depending on visibility.
Rayleigh Scattering Explained
- Proposed by Nobel laureate Lord Rayleigh in the 19th century.
- Explains how light interacts with particles smaller than its wavelength.
- Intensity of scattering is inversely proportional to wavelength.
- This is also why Earth’s sky appears blue, as blue light scatters more than red.
Significance of Blood Moon
- Offers a natural laboratory to study Earth’s atmosphere.
- Provides opportunities for astronomical observation and public engagement with science.
- Holds cultural and mythological importance across civilizations.
Conclusion:
A Blood Moon is not just a celestial spectacle but also an important event for science, helping us understand Earth’s atmosphere and the interaction of light with matter.





