The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has released ‘Model Rules for Felling of Trees in Agricultural Lands’ to simplify tree felling regulations and boost agroforestry practices in States and UTs.
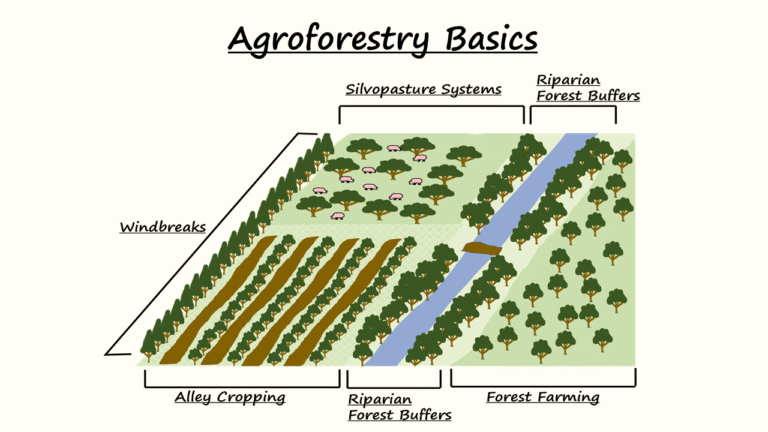
What is Agroforestry?
- Agroforestry is the practice of growing trees and crops together on the same piece of land.
- It supports environmental conservation, improves farm productivity, and helps in income generation for farmers.
Benefits of Agroforestry
- Climate Benefits: Acts as a carbon sink by absorbing greenhouse gases. Offers microclimate control, such as shade and windbreaks.
- Water Conservation: Tree roots help in absorbing excess rainwater and recharging groundwater.
- Income & Livelihood: Yields non-timber products like fruits, bamboo, medicinal plants, etc. Adds economic value for small and marginal farmers.
Status in India
- Agroforestry covers 8.65% of India’s land area.
- Major states: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh.
- India has vast potential as 56% of land is farmland, and 20% is forest.
Model Rules for Felling of Trees
- Issued as guidelines to help States frame their own simplified rules.
- Key Features:
- Managed by a State-level Committee under 2016 wood-based industries guidelines.
- Includes:
- Registration of plantations.
- Monitoring of tree-felling.
- Promoting farm-grown timber trade.
- National Timber Management System (NTMS) portal to handle applications.
Tree Felling Procedure
- For less than 10 trees: Upload tree photos on NTMS –Auto-generated NOC.
- For more than 10 trees: Online application –Field inspection by agency-Permit generation.
Government Schemes Supporting Agroforestry
- National Agroforestry Policy (2014): Encourages tree-based farming for better productivity and incomes.
- PM Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY): Promotes water-efficient farming with agroforestry models.
- National Bamboo Mission (2018): Focuses on bamboo cultivation to support rural livelihoods.
- Sub-Mission on Agroforestry (SMAF): Gives financial support under the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Integrated Farming System (IFS): Combines crops, livestock, and trees for resource efficiency and climate resilience.
Way Forward
- Incentives for Farmers: Offer insurance, financial support, and guaranteed buyers.
- Transparent Monitoring: Use audits and real-time tracking to prevent misuse.
- Eco-Policy Integration: Include agroforestry in climate action and rural development plans.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry can support sustainable agriculture, climate goals, and rural development. With simplified rules and government backing, it offers a win-win solution for farmers and the environment.





