Countries are moving forward to implement the High Seas Treaty, formally called the Agreement on Marine Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ), aimed at conserving biodiversity in international waters and ensuring equitable benefit sharing.
About BBNJ Agreement:
- Full Form: Agreement on Marine Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction.
- Purpose: First treaty dedicated to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in the high seas, treating it as the common heritage of humankind.
- Timeline:
- Negotiated under UNCLOS for over 10 years.
- Finalised in 2023, opened for signing in 2024.
- India signed the agreement in 2024.
- Treaty becomes legally binding 120 days after the 60th ratification.
Key Components of the Treaty:
- Marine Genetic Resources (MGRs): Regulation and fair sharing of benefits from high-seas genetic resources.
- Area-Based Management Tools (ABMTs): Including Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) to conserve biodiversity.
- Capacity Building & Technology Transfer: Supporting developing countries in research, monitoring, and sustainable use.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Ensuring activities do not harm marine ecosystems.
Preparatory Steps:
- PrepCom I (April 2025): Discussed operational rules, governance, and financing arrangements.
- PrepCom II: Held at the UN with 200+ representatives from governments, civil society, and international organisations.
- Ratifications: Small island nations Cabo Verde and Saint Kitts & Nevis ratified; only five more ratifications needed for entry into force.
- COP1: First decision-making meeting expected late 2026.
Significance of the Treaty:
- No Sovereign Claims: Countries cannot claim or exploit high seas resources exclusively.
- Ecosystem-Based Approach: Promotes precautionary principle and use of traditional & scientific knowledge.
- Environmental Protection: Minimises ecological impacts using ABMTs and EIAs.
- Contribution to SDGs: Supports SDG 14 – Life Below Water by conserving marine biodiversity.
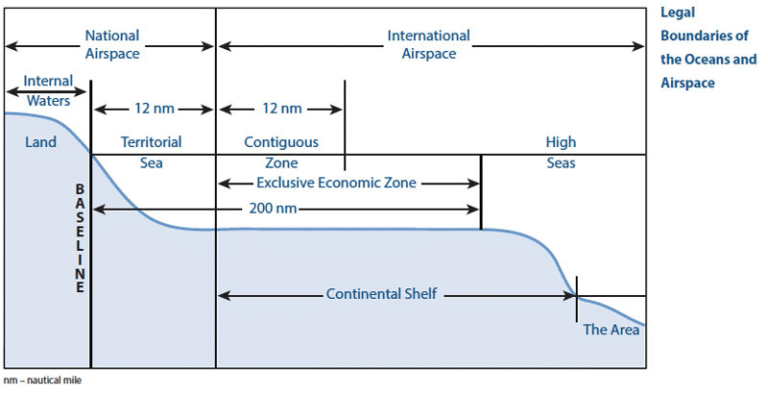
About High Seas:
- Definition: Ocean areas outside territorial waters, exclusive economic zones, internal waters, and archipelagic waters.
- Coverage: 95% of Earth’s ocean habitat by volume; largely unprotected.
Role of UNCLOS & ISA:
- UNCLOS (1982): Governs the law of the sea, regulating all uses of oceans and resources; came into force in 1994.
- International Seabed Authority (ISA):
- Autonomous body established under UNCLOS and 1994 Implementation Agreement.
- Members: 170 states, including India.
- Headquarters: Kingston, Jamaica.
- Regulates mining and related activities on the seabed beyond national jurisdiction.
Way Forward:
- Encourage rapid ratifications to bring the treaty into force.
- Support capacity building for developing nations to participate effectively.
- Ensure equitable benefit sharing and protection of marine biodiversity in global waters.
Conclusion:
The BBNJ Agreement is a landmark treaty to conserve and sustainably use marine biodiversity in international waters, ensuring fair benefit-sharing, protecting ecosystems, and supporting global commitments like SDG14. It strengthens international cooperation for the high seas while safeguarding the interests of developing countries.





