The Human Development Index (HDI), developed by UNDP, is a composite measure that evaluates development beyond GDP, focusing on people’s health, education, and living standards. The 2025 Human Development Report placed India at 130th rank with an HDI value of 0.685, showing progress but highlighting inequality.
Human Development Index (HDI),
- Introduced by UNDP in 1990, inspired by Mahbub ul Haq and Amartya Sen.
- Measures human well-being rather than just economic growth.
- Score ranges between 0 and 1, with higher values indicating better development.
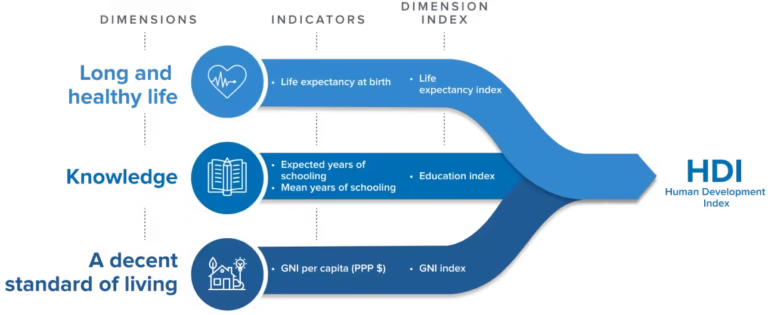
Calculation Method
- Health Dimension: Life expectancy at birth.
- Education Dimension: Mean years of schooling (adults) + expected years of schooling (children).
- Income Dimension: Gross National Income (GNI) per capita (PPP).
- Formula: HDI = Geometric mean of the three indices.
Classification of Countries
- Very High HDI: 0.800 and above.
- High HDI: 0.700–0.799.
- Medium HDI: 0.550–0.699.
- Low HDI: Below 0.550.
India’s Performance (2025 Report)
- HDI Value: 0.685 (2023), rank 130/193 → Medium Human Development.
- Life Expectancy: 72 years (up from 58.6 in 1990).
- Education: Mean years of schooling rose from 3.0 (1990) to 6.2 (2023).
- Income: GNI per capita (PPP) increased from US$2,000 (1990) to ~US$9,000 (2023).
- Inequality Impact: India loses ~31% of HDI value when adjusted for inequality (IHDI).
- Regional Variation: Kerala, Goa, Himachal Pradesh perform better; Bihar, UP, Jharkhand lag behind.
Government Initiatives to Improve HDI
- Ayushman Bharat (2018): Expands healthcare access.
- National Education Policy (2020): Inclusive and skill-based learning.
- Skill India Mission (2015): Vocational training for youth.
- PM-KISAN & PM Awas Yojana: Rural income and housing support.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (2015): Promotes girls’ education.
- Digital India Mission: Improves access to technology and governance.
Challenges
- Oversimplifies complex realities into one number.
- Does not capture environment, governance, or informal work.
- Regional and gender inequalities remain hidden in overall score.
Conclusion
The HDI highlights India’s steady progress in health, education, and income, but also exposes deep inequalities and regional gaps. For sustainable human development, India must focus on inclusive growth, quality education, health equity, and climate resilience.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.