Recent research on Mount Etna analyzed the ratio of small to large earthquakes beneath the volcano, revealing a strong link with its activity over the past 20 years.
Overview:
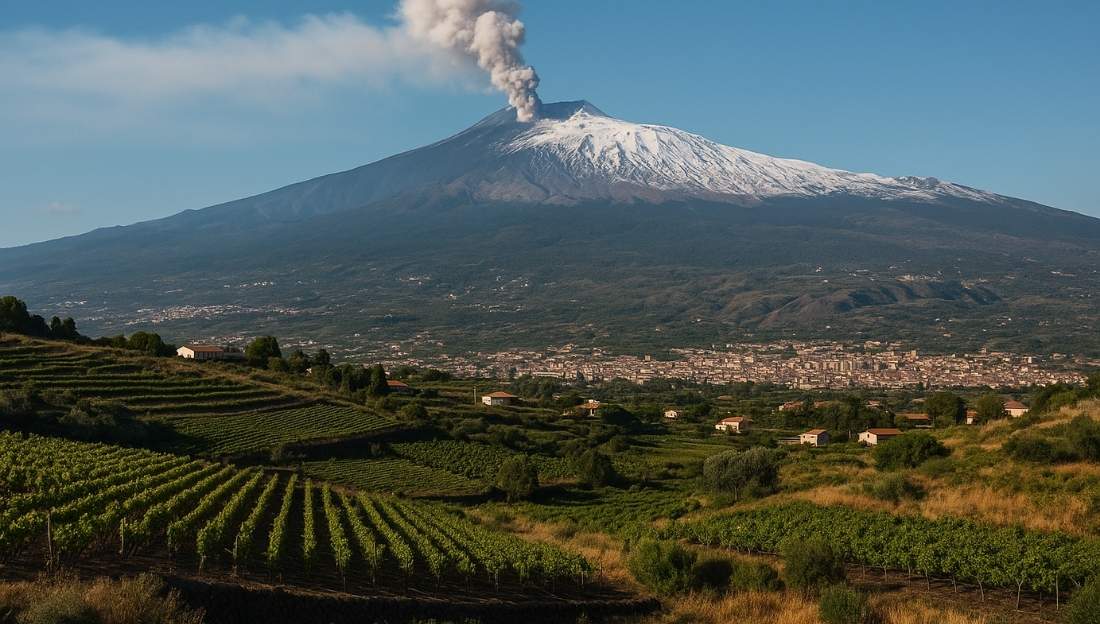
- Mount Etna is an active stratovolcano situated on Sicily, an island in the Mediterranean Sea, part of Italy.
- It is located above the convergent boundary where the African Plate meets the Eurasian Plate.
- The volcano is the tallest active volcano in Europe and the highest peak in Italy south of the Alps.
- Height: approximately 3,350 meters (11,000 feet).
- Area: covers about 1,190 sq. km with a basal circumference of 140 km.

Geological Significance:
- Classified as a stratovolcano, characterized by alternating layers of lava and ash.
- Its eruptions are influenced by tectonic activity at the African-Eurasian plate margin.
- The eruptive history extends back around 500,000 years, with at least 2,700 years of documented eruptions.
Cultural and Historical Importance:
- Mount Etna has inspired numerous legends in ancient Greek mythology.
- It is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its geological and cultural significance.
Recent Developments:
- Studies show that the ratio of minor to major earthquakes under Mount Etna strongly correlates with volcanic activity.
- Understanding these seismic patterns helps predict potential eruptions and manage risks for nearby communities.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.