ISRO announced that Aditya-L1, India’s first solar observatory, helped scientists understand the unusual behaviour of the May 2024 solar storm, one of the strongest in over 20 years. The mission provided crucial real-time data that explained why the storm’s impact on Earth did not follow typical patterns.
Solar Storm
- A solar storm refers to a sudden outburst of charged particles, magnetic energy, and radiation released from the Sun into space.
- These disturbances arise when the Sun’s magnetic fields become unstable and eject large amounts of energy outward.
What Triggers a Solar Storm?
- The Sun has constantly shifting and tangled magnetic field lines.
- Its equator spins faster than its poles, causing magnetic fields to twist and overstretch.
- When these twisted fields break and reconnect (magnetic reconnection), massive energy is released.
- This eruption may produce:
– Solar flares (intense flashes of light)
– Radiation storms (high-speed charged particles)
– Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) — giant clouds of plasma thrown into space
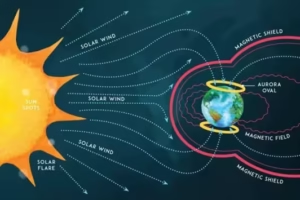
Impacts of Solar Storms on Earth
- If directed toward Earth, they disturb Earth’s magnetic field and create geomagnetic storms.
Effects may include:
– Radio communication failures
– GPS disturbances
– Power grid malfunctions
– Formation of bright auroras - Humans on Earth remain safe due to the protective atmosphere and magnetic field, which block harmful radiation.
- Solar Flares: These are powerful bursts of radiation across the entire electromagnetic spectrum — from X-rays and gamma rays to visible light. The strongest flares carry energy equal to billions of hydrogen bombs.
- Radiation Storms: Solar eruptions can accelerate electrons and protons to extremely high speeds. The fastest particles can reach Earth in 30 minutes, affecting satellites and astronaut safety.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
- CMEs are massive clouds of electrically charged gas (plasma) erupting from the Sun’s corona.
- A single CME can eject billions of tons of material, forming huge bubble-like structures.
Conclusion
- India’s first dedicated solar observatory, launched by ISRO on 2 September 2023.
- Positioned in a halo orbit around Lagrange Point L1, about 1.5 million km from Earth.
- From L1, the spacecraft gets an uninterrupted view of the Sun without eclipses.
- Equipped with seven scientific instruments to study the Sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, corona, and solar particles.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.