A recent car explosion near Delhi’s Red Fort has exposed a new trend of terrorists using advanced digital technologies for planning, funding, and execution highlights the growing shift toward encrypted and covert digital platforms.
Shift to Digital Tradecraft
- Terrorists are using secure and encrypted platforms like Threema, VPNs, cloud servers, and closed online communities.
- These platforms do not require phone numbers or identity proof, protecting terrorists from surveillance.
- They are also using dark web tools, virtual private servers, and bypassing traditional monitoring methods.
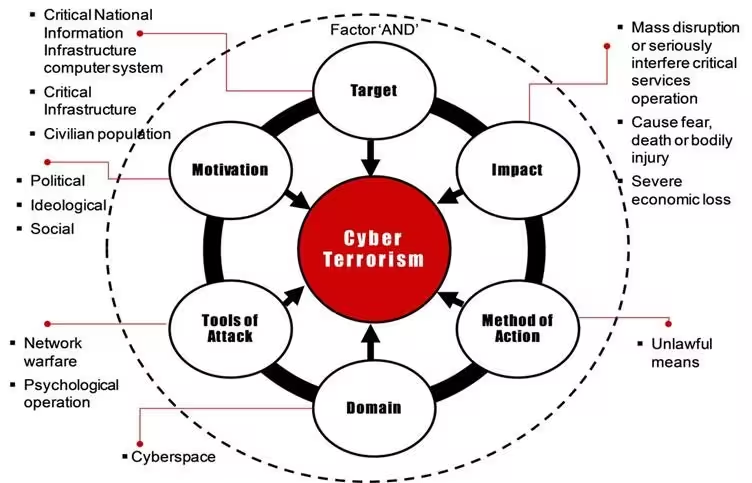
Features of Digital Terrorism
- Encrypted Communication: Messaging apps with end-to-end encryption reduce traceability. Some don’t need SIM cards or identity proof, making monitoring difficult.
- Digital Secrecy and Anonymity: Use of VPNs, proxies, and encrypted cloud servers hides location and identity. Terrorists create private networks for planning, coordination, and data sharing.
- Operational Discipline: Completely avoids traceable methods like mobile phones and public internet. Use of isolated offline networks, code names, and hidden digital storage.
- Emerging Technologies: Use of AI, deepfake tools, cryptocurrency, and memory-wiping technologies. Digital financial transfers leave minimal physical evidence.
Implications for National Security
- Traditional surveillance methods like tapping phones, tracking SIMs, and email monitoring are becoming ineffective.
- Digital anonymity reduces the ability of law enforcement to track suspects.
- Terror attacks may involve fewer people physically, but more digital actors operating remotely.
- Radicalisation, recruitment, and training can occur entirely in the digital space.
Challenges for Law Enforcement
- Lack of trained digital forensic teams.
- Limited cooperation between agencies and low investment in cyber surveillance.
- Poor coordination between national security bodies and private tech companies.
- Legal and policy frameworks have not adapted to encrypted digital ecosystems.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Digital Forensics Teams to track online activities, decode encrypted platforms, and monitor remote operations.
- Create Strong Cyber Laws to regulate encrypted communication platforms and enhance accountability of service providers.
- Enhance Inter-agency Coordination between intelligence, police, cybercrime units, and international agencies.
- Public Awareness and Digital Literacy to prevent exploitation of vulnerable individuals online.
- Promote Tech Collaboration with AI, data analytics, and predictive policing tools.
Conclusion
Digital terrorism represents a silent yet powerful threat, operating beyond physical borders. To counter this, India must shift from traditional intelligence to a technology-driven approach, combining cyber skills, strong laws, and coordinated action.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.





