The SAIME Initiative, developed in the Sundarbans by the Nature Environment and Wildlife Society (NEWS), has received Global Technical Recognition from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) for integrating sustainable aquaculture with mangrove restoration.
About SAIME Initiative
- Concept: A multi-stakeholder model combining shrimp farming with mangrove conservation to support livelihoods while restoring ecosystems.
- Implementing Agencies: NEWS, with support from Global Nature Fund (Germany), Naturland, and Bangladesh Environment & Development Society (BEDS).
- Purpose: Promotes climate-adaptive, low-impact aquaculture, balancing ecological health with local economic growth.
- Coverage & Impact:
- Operates on 29.84 hectares with 42 fish farmers.
- Achieved a 100% increase in net profits through eco-friendly, low-input methods.
- Target Group: Focuses on climate-vulnerable coastal communities, promoting chemical-free shrimp farming to build resilience.
Core Features and Approach
- Ecosystem Integration: Maintains 5–30% mangrove cover in aquaculture ponds to link productivity with ecosystem restoration.
- Community Participation: Uses a bottom-up co-management model, involving local farmers in planning, monitoring, and benefit-sharing.
- Sustainable Practices: Mangrove litter is used as shrimp feed, reducing chemical use and enhancing natural nutrient cycles.
- Environmental Benefits: Supports carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and the blue carbon economy.
- Global Alignment: Contributes to SDG-13 (Climate Action), SDG-14 (Life Below Water), and SDG-15 (Life on Land).
Significance
- Demonstrates climate-smart, nature-based livelihood solutions.
- Encourages community-led conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
- Enhances coastal resilience, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration, aligning local actions with global sustainability goals.
SUNDARBANS
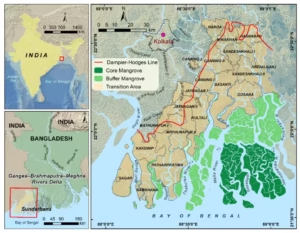
- Location: South and North 24-Parganas, West Bengal; southern tip of Gangetic Delta.
- Area: 2,585.89 sq km, proposed expansion to 3,629.57 sq km; world’s largest mangrove forest.
- Status: Tiger Reserve, National Park, Biosphere Reserve, UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Topography: Dense tidal creeks, estuaries, 105 mangrove-covered islands.
- Flora: Dominated by Avicennia, Rhizophora, Sonneratia, Heritiera species.
- Fauna: Royal Bengal Tiger, Fishing Cat, Estuarine Crocodile, Irrawaddy Dolphin, King Cobra, endangered birds.
- Ecological Importance: Acts as a natural barrier against cyclones and tsunamis, carbon-rich ecosystem, and nursery ground for fisheries — crucial for India’s blue economy and coastal resilience.
Conclusion
While Punjab’s floods caused serious damage, the state’s soils remain recoverable with prompt scientific management. Through soil testing, organic amendments, and community-level interventions, Punjab can restore soil health and sustain its agricultural resilience in the coming rabi season.
This topic is available in detail on our main website.





